Understanding the average height of women in the United States is more than just a statistical curiosity. It reflects broader health trends, lifestyle choices, and genetic factors that influence human development. The average height of women in the U.S. has become a focal point for researchers, policymakers, and the general public alike. This article will delve into the intricacies of this topic, providing you with valuable insights and data-driven conclusions.
Height is a fundamental aspect of human physiology, and its measurement plays a significant role in health assessments and societal norms. In the United States, the average height of women has been a subject of interest for decades. From understanding the factors that contribute to height to examining how it impacts daily life, this topic encompasses a wide range of discussions.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about the average height of women in the United States. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the topic, backed by reliable data and expert insights.
Read also:Exploring Deva Cassels Eye Color A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Historical Perspective on Women's Height
- Current Statistics on Average Height
- Genetic Factors Influencing Height
- Environmental Factors Affecting Height
- Health Implications of Height
- Regional Variations in Women's Height
- Comparison with Global Standards
- Trends Over Time
- Factors Impacting Height Growth
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Historical Perspective on Women's Height
The average height of women in the United States has evolved over the years. Historical records indicate that women in the early 20th century were generally shorter than their modern counterparts. This shift can be attributed to advancements in healthcare, nutrition, and living conditions.
During the 1900s, the average height of women was approximately 5 feet 2 inches (157 cm). However, with improvements in public health and nutrition, this figure has gradually increased. By the mid-20th century, the average height had risen to around 5 feet 3 inches (160 cm).
Key Milestones in Height Trends
- Early 1900s: Average height of women was around 5 feet 2 inches.
- Mid-1900s: Height increased to approximately 5 feet 3 inches.
- 2000s: Modern average height stabilized at 5 feet 4 inches.
These milestones highlight the significant progress in living conditions and healthcare that have influenced height trends over the decades.
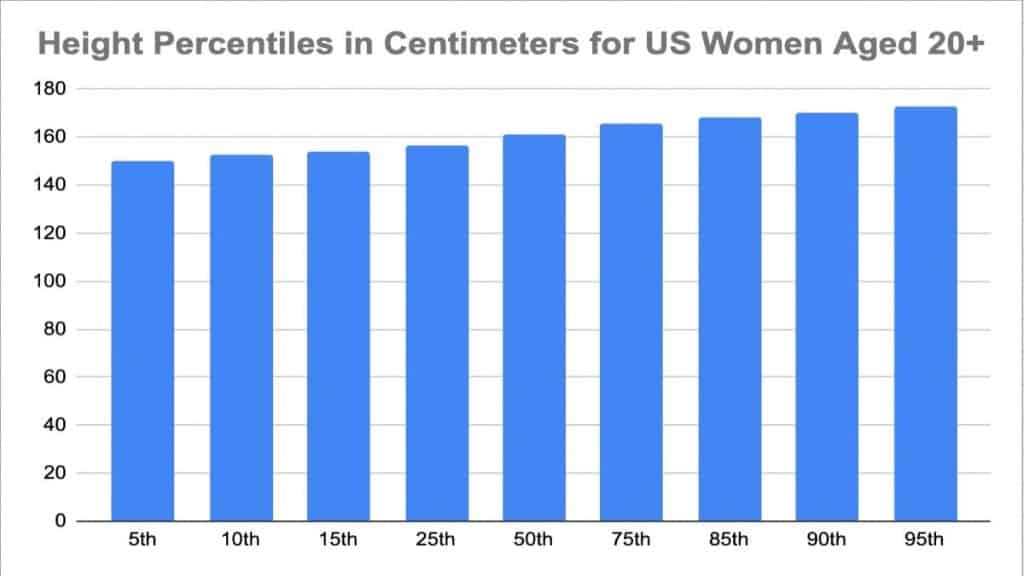
Current Statistics on Average Height
As of recent data, the average height of women in the United States is approximately 5 feet 4 inches (162.5 cm). This figure is based on comprehensive studies conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other authoritative sources.
Interestingly, the average height varies slightly depending on age groups and ethnic backgrounds. For instance, younger women tend to be slightly taller due to better access to nutrition and healthcare during their formative years.
Key Data Points
- Average height: 5 feet 4 inches (162.5 cm).
- Variations by ethnicity: Some groups report slightly different averages.
These statistics underscore the importance of understanding height as a multifaceted phenomenon influenced by various factors.
Read also:Rachel Levine Real Name Unveiling The Story Of A Trailblazer
Genetic Factors Influencing Height
Genetics plays a crucial role in determining the average height of women in the United States. Studies indicate that approximately 60-80% of height variation is attributed to genetic factors. This means that hereditary traits passed down from parents significantly impact an individual's height potential.
Specific genes, such as those responsible for growth hormone production, contribute to height development. Additionally, variations in DNA sequences can lead to differences in height among individuals.
Key Genetic Influencers
- Growth hormone genes.
- Genetic variations in DNA sequences.
While genetics provides a foundational framework, other factors also play a critical role in determining final height.
Environmental Factors Affecting Height
Beyond genetics, environmental factors significantly influence the average height of women in the United States. Nutrition, healthcare, and socioeconomic conditions all contribute to height development.
Adequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence is particularly important for achieving optimal height. Deficiencies in essential nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, and minerals, can hinder growth. Similarly, access to quality healthcare ensures that developmental issues are addressed promptly.
Impact of Nutrition
- Protein-rich diets promote healthy growth.
- Vitamins and minerals are crucial for bone development.
By addressing these environmental factors, society can help individuals reach their full height potential.
Health Implications of Height
The average height of women in the United States has implications for health and well-being. Taller individuals often experience lower risks of certain health conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes. Conversely, shorter individuals may face increased risks of other conditions, including osteoporosis.
Height also influences social and economic opportunities. Studies suggest that taller individuals may enjoy certain advantages in the workplace and societal interactions. However, it's important to recognize that height is just one of many factors that contribute to overall success and happiness.
Health Risks by Height
- Taller women: Lower risk of heart disease.
- Shorter women: Higher risk of osteoporosis.
Understanding these health implications can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their well-being.
Regional Variations in Women's Height
Within the United States, regional variations exist in the average height of women. These differences can be attributed to variations in genetics, socioeconomic conditions, and access to healthcare.
For instance, women in the Northeast tend to be slightly taller than those in the South, likely due to differences in dietary habits and lifestyle choices. Similarly, urban areas often report higher average heights compared to rural regions, reflecting disparities in resource availability.
Regional Differences
- Northeast: Slightly taller averages.
- South: Slightly shorter averages.
These regional variations highlight the complex interplay of factors that influence height development.
Comparison with Global Standards
When compared to global standards, the average height of women in the United States ranks relatively high. Countries in Northern Europe, such as the Netherlands and Denmark, report the tallest average heights for women, while some Asian and African nations report shorter averages.
Global comparisons provide valuable insights into the broader context of height development. They also highlight the importance of addressing disparities in healthcare and nutrition to ensure equitable growth opportunities for all individuals.
Global Height Rankings
- Netherlands: Tallest average height for women.
- United States: High ranking among global averages.
By learning from global trends, the United States can continue to improve its health and nutrition policies.
Trends Over Time
Examining trends over time reveals important insights into the average height of women in the United States. Data from the past century shows a steady increase in height, driven by improvements in healthcare, nutrition, and living conditions.
However, recent years have seen a plateau in height trends, suggesting that the population may be approaching its genetic height potential. This stabilization underscores the importance of addressing remaining disparities in healthcare and nutrition to ensure equitable growth opportunities for all.
Key Trends
- Steady increase in height from the early 1900s to the mid-2000s.
- Plateau in recent years due to reaching genetic potential.
Understanding these trends helps policymakers and researchers develop strategies to address remaining challenges.
Factors Impacting Height Growth
Several factors impact the growth and development of height in women. In addition to genetics and nutrition, physical activity, sleep patterns, and stress levels all play a role in determining final height.
Regular physical activity during childhood and adolescence promotes healthy bone development and growth. Adequate sleep ensures that the body has sufficient time to repair and grow. Managing stress levels also contributes to overall well-being and optimal growth.
Key Growth Factors
- Physical activity: Promotes bone development.
- Sleep: Essential for growth and repair.
- Stress management: Supports overall well-being.
Addressing these factors can help individuals achieve their full height potential.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the average height of women in the United States is a multifaceted topic influenced by genetics, nutrition, healthcare, and lifestyle factors. By examining historical trends, current statistics, and global comparisons, we gain a deeper understanding of this important aspect of human development.
As society continues to evolve, addressing disparities in healthcare and nutrition remains crucial for ensuring equitable growth opportunities for all individuals. We encourage readers to explore further resources and engage in discussions about height and its implications for health and well-being.
We invite you to leave your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, please share this article with others who may find it informative. Together, we can promote a better understanding of the factors that shape human development and contribute to a healthier society.