Using tampons is a common and effective way for women to manage their menstrual cycles. If you're new to tampons or seeking clarity on how they work, this article will provide a detailed explanation of how tampons are inserted, addressing common concerns, and offering practical tips for beginners. Whether you're curious about the process or looking to enhance your understanding, this guide is here to help.
Tampons have been a popular choice for menstrual hygiene for decades. They offer convenience, discretion, and freedom during menstruation. However, many women and girls may feel uncertain about how to use them correctly. This article will break down the process step by step, ensuring you feel confident and informed.
Throughout this guide, we'll cover everything from the basics of tampon insertion to troubleshooting common issues. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how tampons work and how to use them safely and effectively.
Read also:Sarah Marie Erome The Rise Of A Digital Phenomenon
Table of Contents
- Understanding Tampons
- Step-by-Step Guide: How Tampons Are Inserted
- Types of Tampons and Their Features
- Tips for Beginners
- Common Concerns and Myths
- Health and Safety Considerations
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Alternatives to Tampons
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Understanding Tampons
Tampons are small, cylindrical absorbent products designed to be inserted into the vagina during menstruation. They absorb menstrual flow internally, offering a discreet and effective way to manage periods. The history of tampons dates back thousands of years, with modern tampons becoming widely available in the 20th century.
How Tampons Work
Tampons are made from materials like cotton or rayon, which absorb menstrual blood. They come with an applicator or are inserted manually, depending on the brand and type. Once inserted, the tampon expands slightly to fit the shape of the vagina, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit.
Step-by-Step Guide: How Tampons Are Inserted
Learning how to insert a tampon may seem intimidating at first, but with practice, it becomes a simple and routine process. Follow these steps for a smooth and comfortable experience:
Step 1: Choose the Right Tampon
- Select a tampon with an applicator if you're a beginner.
- Choose the absorbency level based on your flow (light, regular, or super).
Step 2: Get into a Comfortable Position
- Sit on the toilet with your knees apart.
- Alternatively, stand with one foot elevated on the toilet or bathtub edge.
Step 3: Insert the Tampon
- Relax your muscles and hold the tampon applicator by the middle.
- Gently insert the narrow end of the applicator into your vagina at a slight upward angle.
- Push the tampon in until the outer tube is fully inside and the string is hanging outside.
Step 4: Remove the Applicator
- Hold the string and gently pull the applicator out.
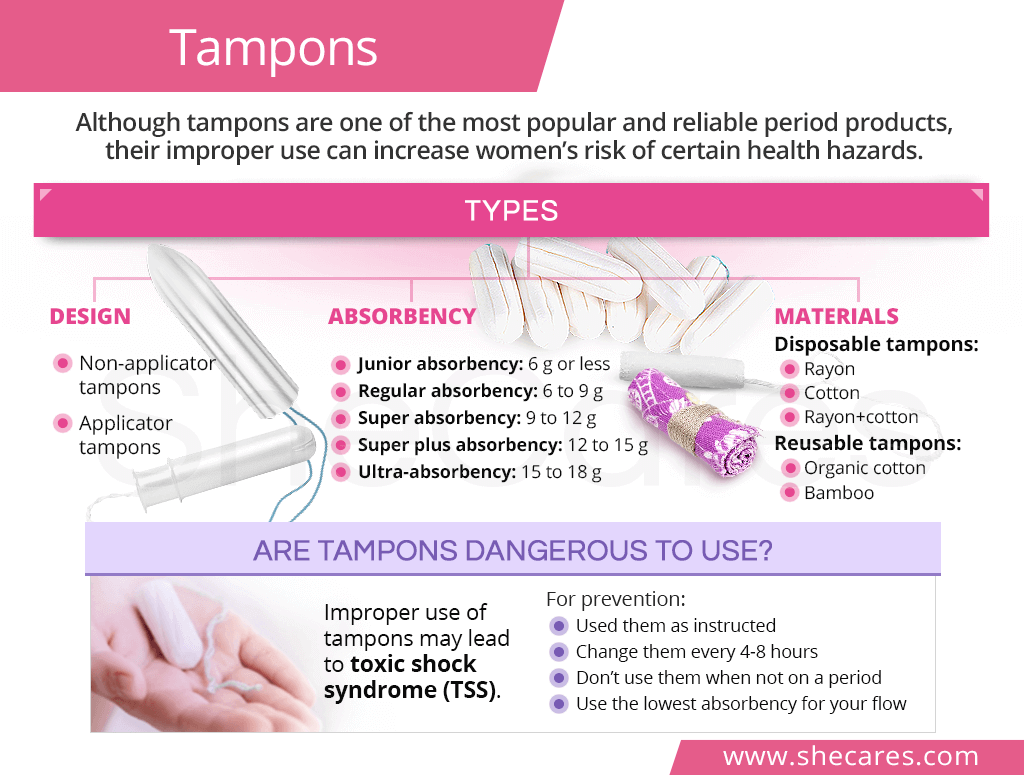
Types of Tampons and Their Features
Not all tampons are created equal. Here's a breakdown of the different types available:
Applicator vs. Non-Applicator Tampons
Applicator tampons come with a plastic or cardboard tube to assist with insertion, while non-applicator tampons require manual insertion. Beginners often prefer applicator tampons for ease of use.
Materials and Absorbency Levels
- Cotton Tampons: Made from 100% cotton, these are hypoallergenic and suitable for sensitive skin.
- Rayon Tampons: More absorbent but may cause irritation in some users.
- Absorbency Levels: Light, regular, super, and super plus options cater to varying menstrual flows.
Tips for Beginners
If you're new to tampons, here are some practical tips to make the transition smoother:
Read also:Christoph Sanders Partner A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Career And Impact
- Practice inserting a tampon when you're not on your period to familiarize yourself with the process.
- Use a mirror to visualize the insertion process if needed.
- Start with a lighter absorbency level to avoid discomfort.
Common Concerns and Myths
Many women have questions and misconceptions about tampons. Let's address some of the most common concerns:
Will a Tampon Affect My Virginity?
No, using a tampon does not affect your virginity. The hymen can stretch to accommodate the tampon without causing any permanent changes.
Can a Tampon Get Lost Inside Me?
No, a tampon cannot get lost inside your body. The vagina is a closed muscular tube with a cervix at the end, which prevents anything from going too far.
Health and Safety Considerations
Using tampons safely is crucial to avoid complications. Here are some important health tips:
Understanding Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Toxic Shock Syndrome is a rare but serious condition associated with tampon use. To reduce the risk:
- Change your tampon every 4-8 hours.
- Avoid using tampons with absorbency higher than necessary.
- Consider alternating tampons with pads during your period.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter difficulties with tampon insertion, here are some solutions:
Tampon Feels Too Tight
Relaxation is key. Take deep breaths and try again in a different position if needed. Using a smaller absorbency level may also help.
Alternatives to Tampons
While tampons are a popular choice, other menstrual products are available:
- Menstrual Cups: Reusable silicone cups that collect menstrual flow.
- Period Underwear: Absorbent underwear designed to replace pads or tampons.
- Reusable Pads: Washable cloth pads for eco-friendly menstrual care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Change My Tampon?
It's recommended to change your tampon every 4-8 hours to maintain hygiene and reduce the risk of TSS.
Can I Swim While Using a Tampon?
Yes, tampons are designed to be worn during activities like swimming. Ensure you change the tampon before and after swimming.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Understanding how tampons are inserted is an essential part of menstrual care. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently use tampons to manage your period. Remember to prioritize your health and safety by changing tampons regularly and being aware of potential risks like TSS.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from it. For more information on menstrual health, explore our other resources. If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment below!
Data and statistics in this article are sourced from reputable organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization.