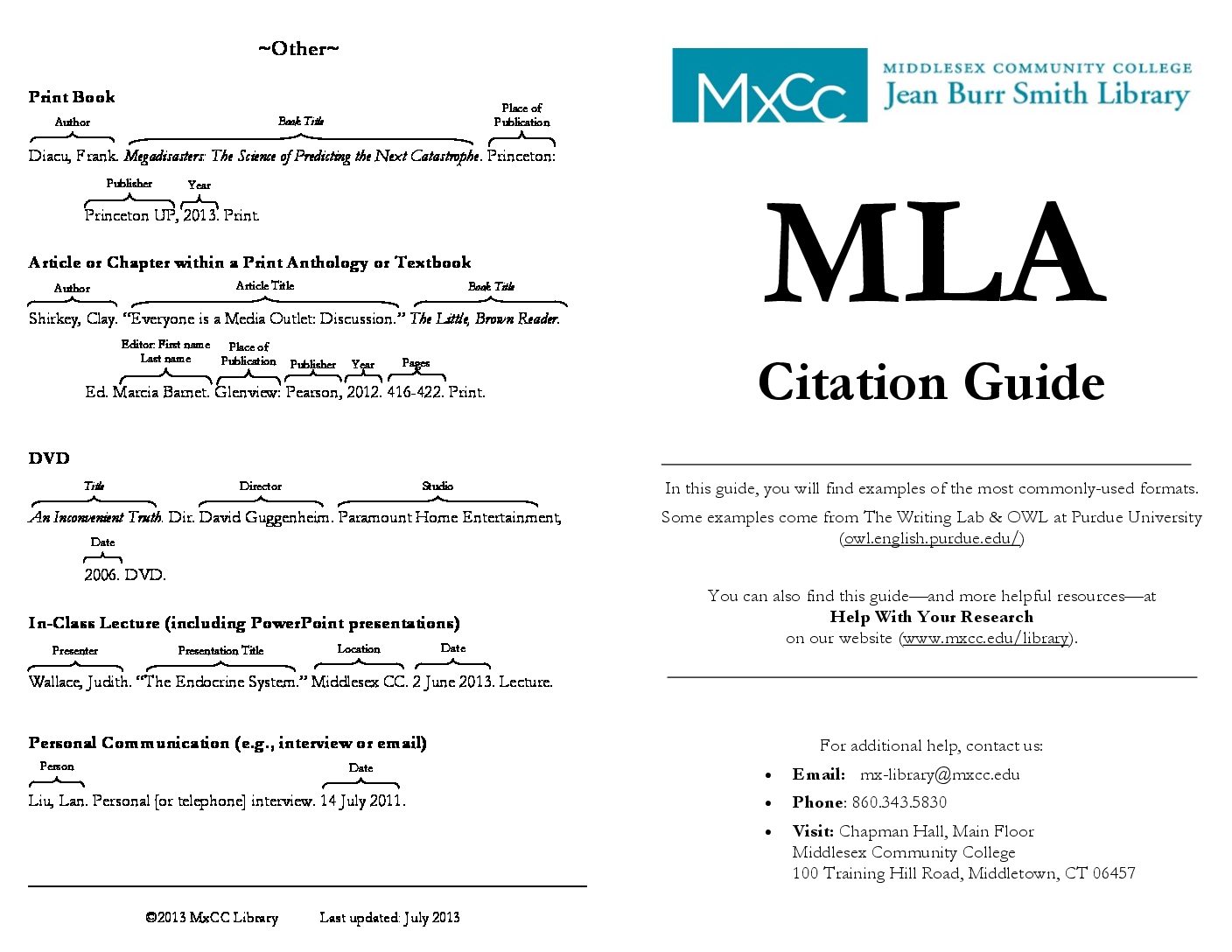
MLA in-text citation is an essential tool for academic writers to acknowledge the sources they use in their work. Proper citation not only strengthens your arguments but also helps avoid plagiarism. Whether you're a student working on an essay or a researcher compiling a scholarly article, understanding how to use MLA in-text citation effectively is crucial.
In today's academic landscape, the ability to correctly cite sources has become increasingly important. As universities and institutions worldwide adopt standardized citation formats, mastering MLA in-text citation becomes a fundamental skill for anyone involved in academic writing. This guide will walk you through the basics and nuances of MLA in-text citation, ensuring you have a solid foundation for your academic work.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of MLA in-text citation, including its rules, variations, and practical applications. Let's dive into the details and equip yourself with the knowledge to enhance your academic writing.
Read also:Albert Brown Iv A Comprehensive Look At His Life Achievements And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is MLA In-Text Citation?
- Basic Format of MLA In-Text Citation
- Common Examples of MLA In-Text Citation
- Variations in MLA In-Text Citation
- Handling Multiple Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism Through Proper Citation
- MLA Style Guidelines and Best Practices
- Citing Digital Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions About MLA In-Text Citation
- Conclusion
What is MLA In-Text Citation?
The Modern Language Association (MLA) style is widely used in the humanities, particularly in literature, language, and cultural studies. MLA in-text citation is a method of acknowledging the sources you use within the body of your text. It involves providing brief references directly in your writing, allowing readers to locate the full source information in the Works Cited page.
This citation style emphasizes simplicity and clarity, making it accessible for both writers and readers. The core principle of MLA in-text citation is to provide enough information within the text so that readers can easily find the corresponding entry in the Works Cited list.
Why Use MLA In-Text Citation?
MLA in-text citation serves several important purposes:
- It gives credit to the original authors whose work you are referencing.
- It helps maintain academic integrity by avoiding unintentional plagiarism.
- It enhances the credibility of your writing by demonstrating that your arguments are supported by reliable sources.
Basic Format of MLA In-Text Citation
The basic format for MLA in-text citation includes the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the information was taken. This information is placed in parentheses at the end of the sentence or clause it refers to. For example:
According to Smith, "Effective communication is essential in academic writing" (45).
Components of the Basic Format
Here are the key components of the basic MLA in-text citation format:
Read also:Dress To Impress Crystal Couture Elevate Your Style With Exquisite Designs
- Author's Last Name: Always include the last name of the author whose work you are citing.
- Page Number(s): Include the page number(s) where the cited information can be found. Do not include "p." or "pp." before the page numbers.
Common Examples of MLA In-Text Citation
Understanding how to apply MLA in-text citation in different scenarios is essential for accurate referencing. Below are some common examples:
Example 1: Single Author
When citing a work by a single author, include the author's last name and the page number:
Johnson argues that "critical thinking is a skill that can be developed over time" (12).
Example 2: Multiple Authors
If a source has two or three authors, include all their last names in the citation:
Research by Brown, Davis, and Lee shows that "collaborative learning enhances student engagement" (78).
Variations in MLA In-Text Citation
MLA in-text citation can vary depending on the type of source being cited. Below are some variations you may encounter:
Variation 1: No Page Numbers
If the source does not have page numbers (e.g., an online article), omit the page number from the citation:
According to Thompson, "digital literacy is becoming increasingly important in the modern world" (Thompson).
Variation 2: Indirect Sources
When citing information from a secondary source, include both the original author and the source you are citing:
As cited in Anderson, Johnson argues that "education reform is necessary to address current challenges" (qtd. in Anderson 34).
Handling Multiple Sources
When citing multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the sources with a semicolon:
Various studies suggest that "environmental awareness is growing among younger generations" (Smith 56; Johnson 89).
Tips for Managing Multiple Sources
Here are some tips for handling multiple sources effectively:
- Ensure each source is clearly identified in the citation.
- Organize the sources in alphabetical order based on the authors' last names.
- Double-check the Works Cited page to ensure all sources are accurately listed.
Avoiding Plagiarism Through Proper Citation
Plagiarism is a serious academic offense that can have significant consequences. By using MLA in-text citation correctly, you can avoid unintentional plagiarism and give proper credit to the original authors. Here are some strategies to help you avoid plagiarism:
- Always cite any information that is not your own, even if it is paraphrased.
- Use quotation marks when directly quoting text from a source.
- Keep track of all sources you consult during your research to ensure they are properly cited.
MLA Style Guidelines and Best Practices
Following MLA style guidelines ensures consistency and professionalism in your writing. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman, and set the font size to 12 points.
- Include a header with your last name and page number in the top right corner of each page.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the document.
Additional MLA Style Tips
Here are some additional tips for adhering to MLA style:
- Double-space the entire document, including the Works Cited page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use italics for the titles of longer works, such as books or journals.
Citing Digital Sources
With the increasing prevalence of digital sources, understanding how to cite them properly is crucial. Below are some guidelines for citing digital sources in MLA format:
Example: Citing a Website
If you are citing a website, include the author's name (if available), the title of the webpage, the title of the website, the publication date, and the URL:
According to the article, "The Benefits of Online Learning," "digital education offers flexibility and accessibility" ("Benefits").
Example: Citing an Online Article
For online articles, include the author's name, the article title, the journal or publication name, the publication date, and the DOI or URL:
Research by Martinez indicates that "remote work has become a viable option for many professionals" (Martinez).
Frequently Asked Questions About MLA In-Text Citation
Here are some common questions about MLA in-text citation:
Q1: Do I need to include the author's name in the citation?
Yes, the author's last name is a required component of MLA in-text citation unless the author is already mentioned in the sentence.
Q2: What if the source has no author?
If the source does not have an author, use the title of the work in the citation. Shorten the title if necessary.
Conclusion
MLA in-text citation is a vital tool for academic writers to acknowledge the sources they use in their work. By mastering the basic format, variations, and best practices of MLA in-text citation, you can enhance the quality and credibility of your writing. Remember to always cite your sources properly to avoid plagiarism and maintain academic integrity.
We encourage you to apply the knowledge gained from this guide in your future writing projects. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to leave a comment below. Additionally, consider exploring other resources on our site to deepen your understanding of academic writing and citation styles.
Sources:
- Modern Language Association. MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab. "MLA Formatting and Style Guide." Purdue OWL, Purdue University, 2023.