Space exploration has always fascinated humanity, and one of the most intriguing topics is the distance to Mars. Understanding how far Mars is from Earth and the challenges associated with traveling to this planet has become increasingly relevant as space agencies like NASA and private companies like SpaceX plan future missions. This article dives deep into the science and technology behind Mars exploration, offering insights into the distance between Earth and Mars and its implications for space travel.
The distance to Mars is not constant due to the elliptical orbits of both planets. This dynamic relationship makes space travel to Mars more complex than it seems. Understanding this variability is crucial for planning missions and ensuring their success. Whether you're a space enthusiast or a researcher, this topic offers valuable insights into our solar system's dynamics.
As humanity continues to explore Mars, learning about the distance between Earth and Mars becomes more important. This article will cover everything you need to know about this subject, including the science behind orbital mechanics, the challenges of interplanetary travel, and the potential for future colonization. Let's begin our journey into the mysteries of Mars!
Read also:Daria Sergeyevna Gordeevagrinkova A Detailed Exploration Of Her Life And Achievements
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Mars Distance
- Orbital Mechanics and Mars Distance
- What is the Average Distance to Mars?
- Understanding the Closest Approach of Mars
- Farthest Distance Between Earth and Mars
- How Long Does It Take to Travel to Mars?
- Technology Behind Mars Exploration
- Challenges of Traveling to Mars
- Future Missions to Mars
- Potential for Mars Colonization
- Conclusion
Introduction to Mars Distance
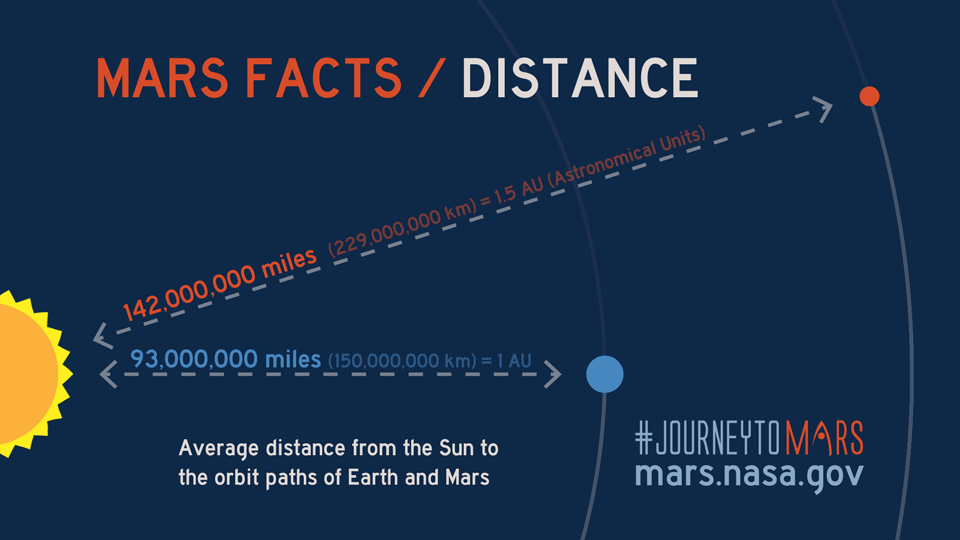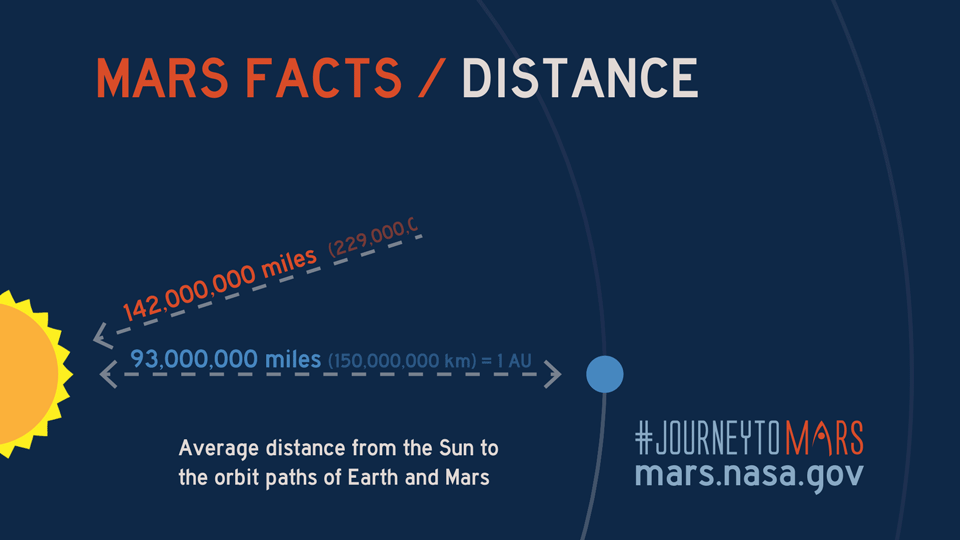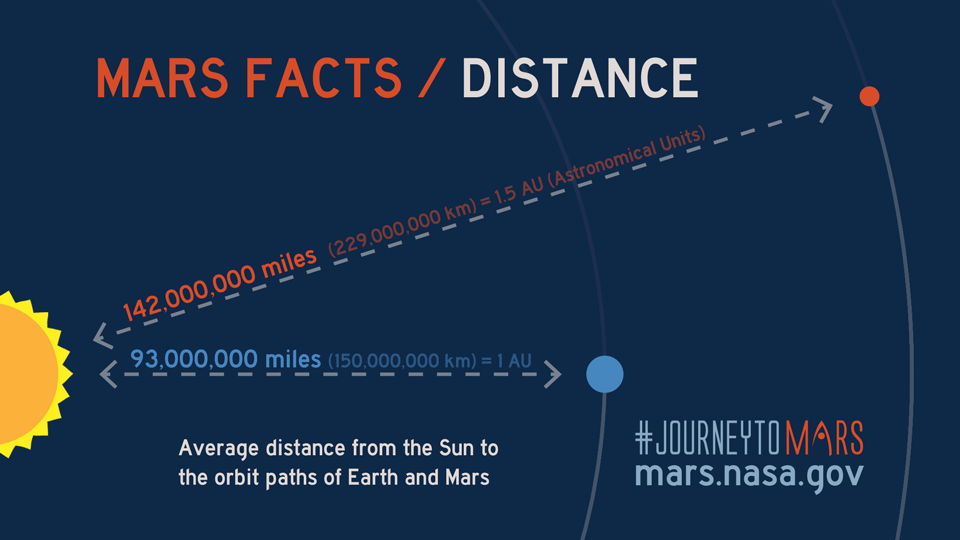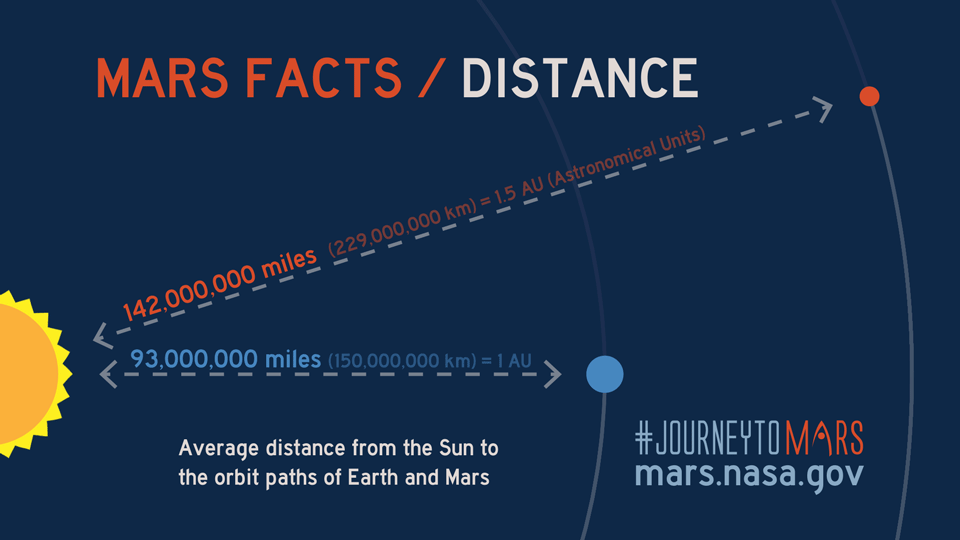
The distance to Mars varies significantly depending on the positions of Earth and Mars in their respective orbits. This variability is a result of the elliptical shape of their orbits around the Sun. At its closest, Mars can be approximately 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles) away from Earth, while at its farthest, the distance increases to about 401 million kilometers (249 million miles).
Understanding the distance to Mars is crucial for planning space missions. Spacecraft need to launch during specific windows when the two planets are in optimal positions relative to each other. These windows, known as launch windows, occur approximately every 26 months, making timing a critical factor in Mars exploration.
Orbital Mechanics and Mars Distance
Orbital mechanics plays a significant role in determining the distance to Mars. Both Earth and Mars follow elliptical orbits around the Sun, which means their distances from the Sun vary throughout the year. This variation affects the distance between the two planets.
Elliptical Orbits
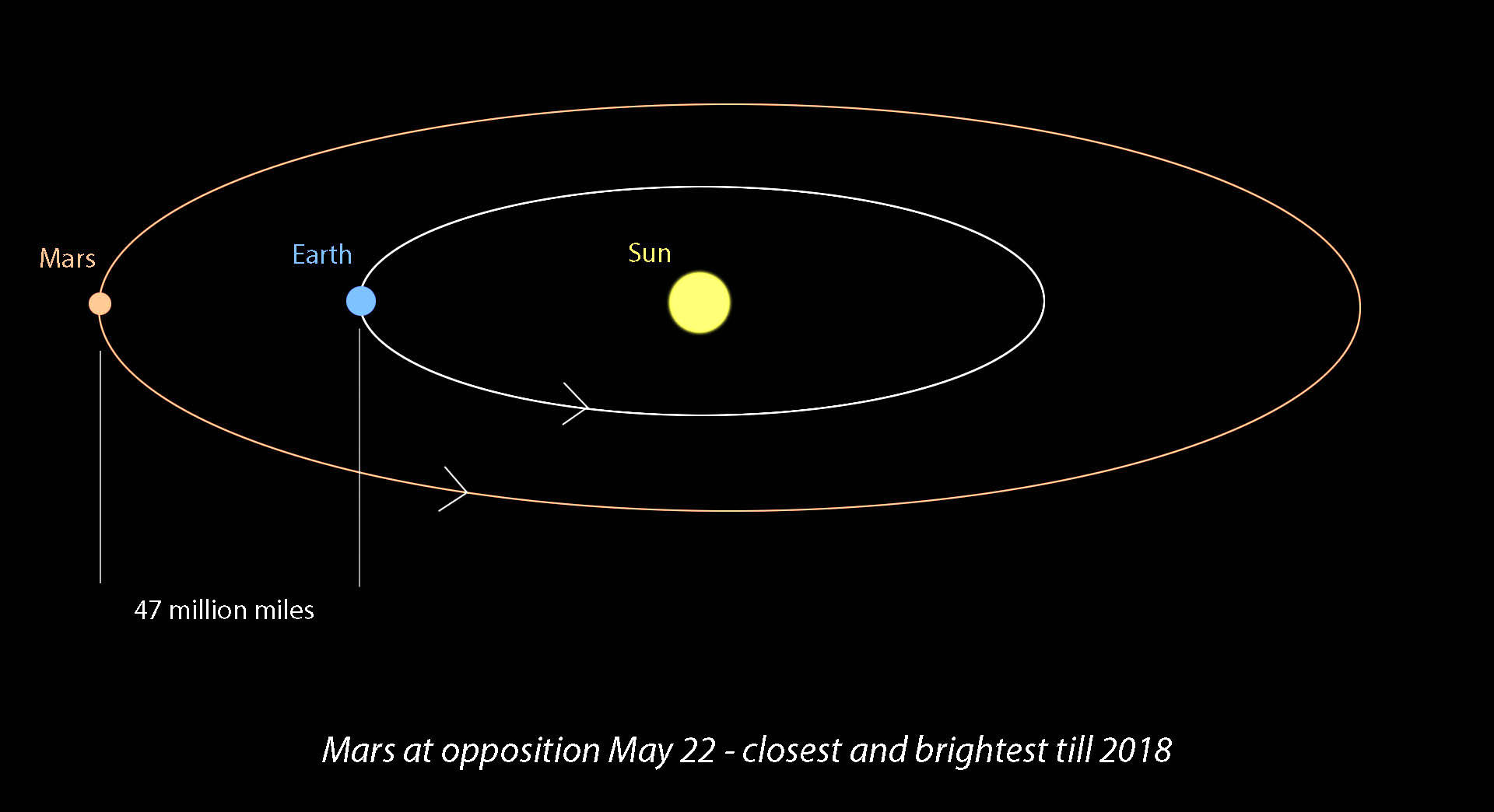
The elliptical nature of planetary orbits means that the distance between Earth and Mars changes constantly. When Earth and Mars are on the same side of the Sun and aligned, the distance is at its minimum, known as opposition. Conversely, when they are on opposite sides of the Sun, the distance is at its maximum.
Opposition and Conjunction
Opposition occurs when Mars and the Sun are on directly opposite sides of Earth. During this time, Mars is closest to Earth, making it the ideal time for launching missions. Conjunction, on the other hand, occurs when Mars and Earth are on opposite sides of the Sun, resulting in the greatest distance between the two planets.
What is the Average Distance to Mars?
The average distance to Mars is approximately 225 million kilometers (140 million miles). This figure represents the midpoint between the closest and farthest distances between the two planets. While this average provides a general idea, the actual distance varies depending on the specific positions of Earth and Mars at any given time.
Read also:Christoph Sanders Partner A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Career And Impact
Scientists use this average distance to calculate the time it takes for spacecraft to travel to Mars and to plan communication delays between Earth and Mars-based missions.
Understanding the Closest Approach of Mars
The closest approach of Mars occurs during opposition, when the planet is nearest to Earth. During this event, the distance can be as little as 54.6 million kilometers (33.9 million miles). This proximity allows for clearer observations of Mars from Earth and optimal conditions for launching spacecraft.
Historical Close Approaches
- In 2003, Mars made its closest approach to Earth in nearly 60,000 years, coming within 55.76 million kilometers (34.65 million miles).
- Another notable close approach occurred in 2018, with Mars coming within 57.6 million kilometers (35.8 million miles).
Farthest Distance Between Earth and Mars
At its farthest, Mars can be up to 401 million kilometers (249 million miles) away from Earth. This distance occurs during conjunction, when Mars and Earth are on opposite sides of the Sun. During this time, communication with Mars-based missions becomes more challenging due to the increased signal delay and potential interference from the Sun.
Impact on Communication
The farthest distance between Earth and Mars affects communication with spacecraft and rovers on the planet. Signals can take up to 24 minutes to travel from Earth to Mars and back, making real-time communication impossible. Space agencies must plan for these delays when designing missions and commanding spacecraft.
How Long Does It Take to Travel to Mars?
The time it takes to travel to Mars depends on the distance between the two planets at the time of launch. On average, a spacecraft takes about six to nine months to reach Mars. This duration can vary based on the specific launch window, mission design, and propulsion technology used.
Factors Affecting Travel Time
- Launch Window: The timing of the launch significantly affects travel time.
- Propulsion Technology: Advanced propulsion systems can reduce travel time, but they come with increased costs and complexity.
- Mission Design: The specific objectives of the mission can influence the chosen trajectory and, consequently, the travel time.
Technology Behind Mars Exploration
Exploring Mars requires cutting-edge technology, from powerful rockets to advanced communication systems. Space agencies and private companies are continually developing new technologies to improve the efficiency and safety of Mars missions.
Spacecraft Design
Spacecraft designed for Mars missions must withstand the harsh conditions of interplanetary travel, including extreme temperatures, radiation, and the vacuum of space. They also need to be equipped with systems for navigation, communication, and scientific experimentation.
Propulsion Systems
Traditional chemical propulsion systems are currently the most commonly used for Mars missions. However, research into alternative propulsion methods, such as ion propulsion and nuclear thermal propulsion, is ongoing. These technologies have the potential to significantly reduce travel time and improve mission capabilities.
Challenges of Traveling to Mars
Traveling to Mars presents numerous challenges, from the technical aspects of spacecraft design to the physiological effects on astronauts. Overcoming these challenges is essential for the success of future Mars missions.
Technical Challenges
- Navigation: Accurately navigating through space requires precise calculations and constant monitoring.
- Communication: The vast distance between Earth and Mars creates delays in communication, complicating mission operations.
- Life Support: Ensuring the survival of astronauts during long-duration missions requires advanced life support systems.
Human Factors
- Psychological Effects: The isolation and confinement of space travel can have significant psychological impacts on astronauts.
- Radiation Exposure: Space radiation poses a serious health risk to astronauts traveling to Mars.
- Physical Health: Microgravity environments can lead to muscle atrophy and bone density loss, requiring countermeasures to maintain astronaut health.
Future Missions to Mars
Several upcoming missions to Mars are planned by space agencies and private companies. These missions aim to further our understanding of the planet and pave the way for human exploration.
NASA's Artemis Program
NASA's Artemis program includes plans for a lunar gateway that will serve as a staging point for future Mars missions. This program aims to develop the technology and infrastructure needed for sustainable exploration of the Moon and Mars.
SpaceX's Starship
SpaceX is developing the Starship, a fully reusable spacecraft designed for interplanetary travel. The Starship is intended to transport humans and cargo to Mars, enabling the establishment of a permanent human presence on the planet.
Potential for Mars Colonization
The idea of colonizing Mars has captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike. While significant challenges remain, advancements in technology and increasing interest from both public and private sectors make Mars colonization a realistic possibility in the future.
Challenges of Colonization
- Habitability: Creating livable environments on Mars requires overcoming extreme temperatures, low atmospheric pressure, and lack of resources.
- Resource Utilization: Developing methods to extract and utilize local resources, such as water and minerals, is crucial for sustainable colonization.
- Health and Safety: Ensuring the long-term health and safety of colonists in the harsh Martian environment is a top priority.
Conclusion
The distance to Mars is a critical factor in space exploration, influencing mission planning, spacecraft design, and communication strategies. Understanding the variability of this distance and the challenges it presents is essential for the success of future missions. As technology advances and interest in Mars exploration grows, the possibility of human colonization becomes increasingly plausible.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the distance to Mars in the comments section below. For more insights into space exploration, check out our other articles on the latest developments in the field. Together, let's continue our journey to uncover the mysteries of the universe!
References:
- NASA Mars Exploration Program
- SpaceX Starship Development
- ESA Mars Missions