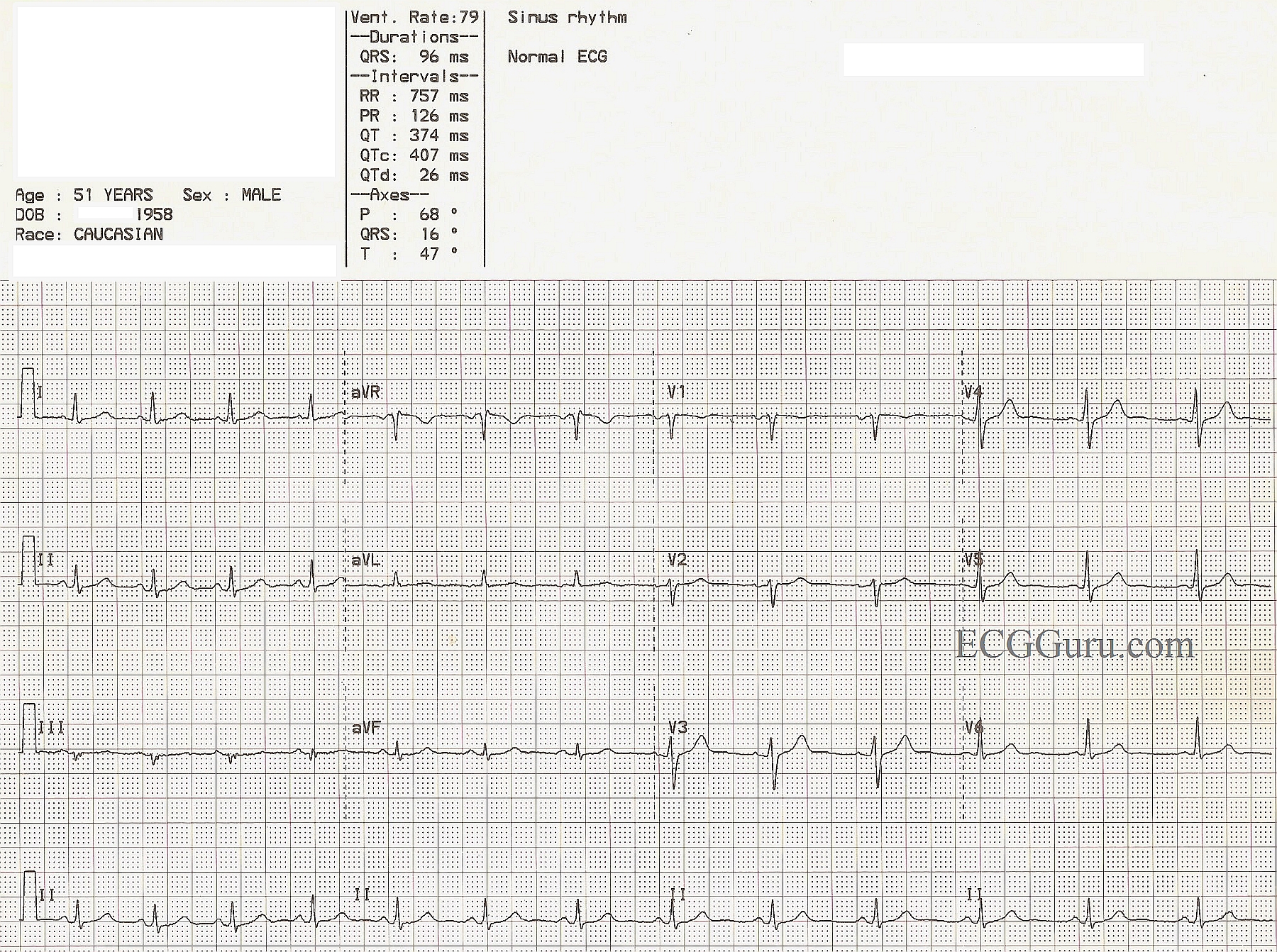
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a crucial diagnostic tool used to monitor and evaluate heart health. It provides vital information about the electrical activity of the heart, helping healthcare professionals identify potential issues before they escalate. If you're interested in learning more about how ECG works, its applications, and why it's essential for cardiovascular health, this article will provide you with all the answers.
Heart conditions are among the leading causes of death globally. Early detection and intervention can significantly reduce the risks associated with these conditions. ECG plays a pivotal role in this process, offering a non-invasive and reliable method to assess heart function. Understanding its role in healthcare can empower individuals to take better care of their heart health.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of ECG, including its history, types, applications, and interpretation. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a student, or someone interested in heart health, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of electrocardiography.
Read also:Hikaru Nag The Rising Star In The World Of Chess
Table of Contents
- Introduction to ECG
- History of Electrocardiography
- Types of ECG Tests
- How ECG Works
- Benefits of Using ECG
- Interpreting ECG Results
- Common Conditions Detected by ECG
- Limitations of ECG
- Advancements in ECG Technology
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to ECG
Electrocardiogram, commonly abbreviated as ECG or EKG, is a diagnostic tool that records the electrical activity of the heart. It is a critical component of modern cardiology and plays a significant role in diagnosing various heart conditions. ECG measures the timing and strength of electrical signals as the heart beats, providing valuable information about heart rhythm, rate, and potential abnormalities.
Doctors use ECG to assess the overall health of the heart and detect issues such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular conditions. It is a painless, non-invasive procedure that can be performed quickly in a clinical setting, making it an essential tool in both emergency and routine care.
Why Is ECG Important?
The importance of ECG lies in its ability to provide real-time data about the heart's electrical activity. This data helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of heart conditions. Early detection of heart problems through ECG can lead to timely interventions, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
History of Electrocardiography
The concept of electrocardiography dates back to the late 19th century when scientists began exploring the electrical activity of the heart. The first successful recording of the heart's electrical signals was achieved by Augustus Waller in 1887. However, it was Willem Einthoven, a Dutch physiologist, who developed the first practical ECG machine in 1903. His work earned him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924.
Key Milestones in ECG Development
- 1887: Augustus Waller records the first human electrocardiogram.
- 1903: Willem Einthoven invents the string galvanometer, laying the foundation for modern ECG.
- 1950s: Advancements in technology lead to the development of portable ECG machines.
- 21st century: Digital advancements enhance the accuracy and accessibility of ECG.
Types of ECG Tests
There are several types of ECG tests, each designed to evaluate different aspects of heart function. The most common types include:
Resting ECG
A resting ECG is performed while the patient is lying down and relaxed. It provides a baseline assessment of heart activity and is often used during routine check-ups.
Read also:Rachel Levine Real Name Unveiling The Story Of A Trailblazer
Stress ECG
Also known as an exercise ECG, this test is conducted while the patient is exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike. It helps identify heart conditions that may only become apparent during physical activity.
Ambulatory ECG
An ambulatory ECG, such as a Holter monitor, records heart activity over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. It is useful for detecting intermittent heart problems that may not be apparent during a standard ECG.
How ECG Works
ECG works by detecting the electrical impulses generated by the heart as it beats. These impulses are transmitted through electrodes placed on the skin and recorded by the ECG machine. The resulting graph, known as an electrocardiogram, displays the heart's electrical activity over time.
The ECG graph consists of waves and intervals that represent different phases of the heart's electrical cycle. By analyzing these patterns, healthcare professionals can identify irregularities and diagnose heart conditions.
Benefits of Using ECG
ECG offers numerous benefits in the field of cardiology. Some of the key advantages include:
- Non-invasive and painless procedure
- Quick and reliable results
- Ability to detect a wide range of heart conditions
- Useful in both emergency and routine care
- Cost-effective diagnostic tool
These benefits make ECG an indispensable tool in modern healthcare.
Interpreting ECG Results
Interpreting ECG results requires specialized knowledge and training. Healthcare professionals analyze various components of the ECG graph, including:
P-Wave
Represents the contraction of the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
QRS Complex
Indicates ventricular depolarization, the process by which the lower chambers of the heart contract.
T-Wave
Reflects ventricular repolarization, the recovery phase after contraction.
By examining these components, doctors can identify abnormalities and diagnose conditions such as arrhythmias, ischemia, and heart block.
Common Conditions Detected by ECG
ECG is instrumental in diagnosing a variety of heart conditions, including:
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats that can be too fast, too slow, or irregular.
- Myocardial Infarction: Commonly known as a heart attack, it occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked.
- Ischemia: Reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, often caused by coronary artery disease.
- Heart Block: A condition where electrical signals between the atria and ventricles are impaired.
Early detection of these conditions through ECG can lead to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Limitations of ECG
While ECG is a powerful diagnostic tool, it does have certain limitations. Some of these include:
- ECG may not detect all heart conditions, especially those that occur intermittently.
- Interpretation of ECG results requires specialized training and expertise.
- External factors such as movement or electrical interference can affect the accuracy of the test.
Despite these limitations, ECG remains a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of heart conditions.
Advancements in ECG Technology
Recent advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the capabilities of ECG. Modern ECG machines are more accurate, portable, and user-friendly than ever before. Innovations such as digital ECG, wearable devices, and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing the field of electrocardiography.
Impact of AI on ECG
Artificial intelligence is being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of ECG interpretation. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of ECG data quickly and identify patterns that may be missed by human observers. This technology has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve patient care.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, ECG is a vital diagnostic tool in the field of cardiology. Its ability to provide real-time data about the heart's electrical activity makes it an indispensable asset in both emergency and routine care. Understanding the importance of ECG and its applications can empower individuals to take better care of their heart health.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the information. For more articles on health and wellness, explore our website and stay informed about the latest developments in healthcare.
Remember, taking care of your heart health is crucial for a long and fulfilling life. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.