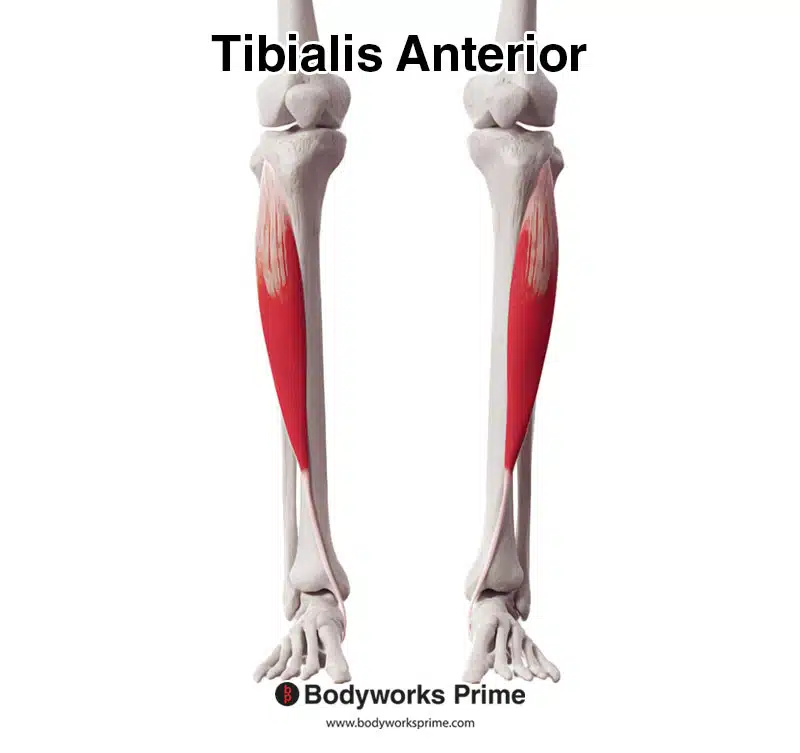
The tibialis anterior plays a crucial role in the movement and stability of the foot and ankle. As one of the primary muscles in the lower leg, it is essential for activities such as walking, running, and maintaining balance. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common conditions related to this muscle can help in preventing and managing injuries.
The importance of the tibialis anterior cannot be overstated when discussing lower limb mobility. This muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot, making it indispensable for everyday movements. By delving into its structure and function, we can better appreciate its significance in biomechanics.
In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the tibialis anterior, its role in movement, common injuries, and effective rehabilitation strategies. Whether you're a healthcare professional, fitness enthusiast, or someone dealing with a related condition, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into maintaining foot and ankle health.
Read also:Noodlemagazine Your Ultimate Guide To Exploring Asian Cuisine And Culture
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
- Function and Movement
- Biomechanics of Tibialis Anterior
- Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Diagnosis and Assessment
- Treatment Options
- Rehabilitation Exercises
- Prevention Strategies
- Nutrition and Recovery
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
The tibialis anterior is a long, spindle-shaped muscle located on the front of the lower leg. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. This muscle is covered by a thin layer of fascia, which provides structural support and flexibility.
Structure and Location
The tibialis anterior is situated in the anterior compartment of the leg, alongside other muscles such as the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. Its location makes it vulnerable to overuse injuries, especially in individuals who engage in repetitive foot movements.
- Origin: Lateral condyle of the tibia
- Insertion: Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones
- Innervation: Deep fibular nerve
- Blood supply: Anterior tibial artery
Function and Movement
As a key player in foot and ankle movement, the tibialis anterior performs two primary actions: dorsiflexion and inversion. These movements are essential for maintaining balance and facilitating smooth transitions during walking and running.
Primary Functions
Dorsiflexion refers to the upward movement of the foot, while inversion involves tilting the sole of the foot inward. Both actions contribute to the stability of the foot and ankle joint, preventing excessive pronation and reducing the risk of injury.
- Dorsiflexion: Essential for heel strike during gait
- Inversion: Helps stabilize the foot during weight-bearing activities
Biomechanics of Tibialis Anterior
The biomechanics of the tibialis anterior are closely tied to its role in gait and posture. During the gait cycle, this muscle works in harmony with other muscles to ensure efficient movement and energy conservation.
Gait Cycle Analysis
In the stance phase of gait, the tibialis anterior assists in lifting the foot off the ground, preparing it for the swing phase. This coordinated movement is crucial for maintaining a natural walking pattern and preventing tripping or stumbling.
Read also:Dress To Impress Crystal Couture Elevate Your Style With Exquisite Designs
Research has shown that individuals with weak tibialis anterior muscles may exhibit altered gait patterns, leading to compensatory movements and increased strain on other parts of the body.
Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Tibialis anterior injuries are relatively common, particularly among athletes and individuals who engage in high-impact activities. These injuries can range from mild strains to more severe conditions like compartment syndrome.
Types of Injuries
- Tibialis anterior tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendon
- Compartment syndrome: Increased pressure in the anterior compartment
- Strains: Overstretching or tearing of the muscle fibers
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, tibialis anterior tendonitis is a prevalent condition among runners and dancers, often caused by repetitive stress on the muscle.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis of tibialis anterior injuries involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and patient history. Healthcare professionals use various techniques to assess the severity of the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic Tools
- Physical examination: Palpation and range of motion testing
- Imaging: X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound
- Functional assessment: Gait analysis and muscle strength testing
A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy highlights the importance of comprehensive evaluation in diagnosing tibialis anterior injuries, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment approaches.
Treatment Options
Treatment for tibialis anterior injuries depends on the severity of the condition and the patient's specific needs. Non-surgical interventions are often the first line of treatment, with surgery reserved for severe cases or those unresponsive to conservative measures.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and activity modification
- Physical therapy and stretching exercises
- Anti-inflammatory medications
In some cases, orthotic devices or braces may be recommended to provide additional support and stability to the foot and ankle.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehabilitation exercises play a crucial role in restoring strength and function to the tibialis anterior. A well-designed program can help prevent future injuries and improve overall performance.
Sample Exercises
- Toe raises: Strengthening the dorsiflexors
- Resistance band exercises: Targeting inversion and dorsiflexion
- Balance training: Enhancing proprioception and stability
Research from the British Journal of Sports Medicine suggests that incorporating eccentric exercises into rehabilitation programs can significantly improve outcomes for patients with tibialis anterior injuries.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing tibialis anterior injuries involves adopting healthy habits and maintaining proper biomechanics. Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of injury.
Key Prevention Tips
- Wear appropriate footwear with adequate support
- Warm up and stretch before physical activity
- Maintain a balanced exercise routine
By prioritizing prevention, individuals can minimize the likelihood of developing tibialis anterior-related issues and maintain optimal foot and ankle health.
Nutrition and Recovery
Nutrition plays a vital role in the recovery process for tibialis anterior injuries. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can accelerate healing and improve overall muscle function.
Key Nutrients for Recovery
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth
- Vitamins and minerals: Support tissue healing and reduce inflammation
- Hydration: Maintains muscle elasticity and joint lubrication
A report from the National Institutes of Health emphasizes the importance of nutrition in injury recovery, highlighting the benefits of a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
Conclusion
The tibialis anterior is a critical muscle for foot and ankle movement, playing a pivotal role in maintaining balance and facilitating smooth transitions during gait. By understanding its anatomy, function, and common injuries, we can better appreciate its significance in biomechanics and injury prevention.
We encourage readers to take proactive steps in maintaining foot and ankle health by incorporating preventive strategies, engaging in regular exercise, and seeking professional guidance when necessary. Feel free to share your thoughts or experiences in the comments section below, or explore other articles on our site for more insights into musculoskeletal health.