In today's real estate market, the age-old question of whether to rent or buy a home continues to challenge many individuals and families. The New York Times Calculator Rent vs Buy has emerged as an invaluable tool to help people make informed decisions about their housing needs. This calculator offers a detailed analysis of various financial factors that play a role in the decision-making process.
With the housing market constantly evolving, understanding the financial implications of renting versus buying is crucial. The New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator simplifies this complex decision by providing personalized insights based on your specific financial situation. Whether you're a first-time homebuyer or a seasoned renter, this tool can help you navigate the complexities of the housing market.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we'll explore how the calculator works, the factors it considers, and how you can use it effectively to make the best decision for your financial future. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the Rent vs Buy Calculator and its significance in the modern housing landscape.
Read also:Jenicka Lopez Net Worth Exploring The Rise Of A Prominent Figure
Table of Contents
- Introduction to New York Times Calculator Rent vs Buy
- How the New York Times Calculator Works
- Key Factors Considered by the Calculator
- Long-Term Benefits of Using the Calculator
- Cost Comparison: Renting vs Buying
- Features of the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using the Calculator
- Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Successful Usage
- Expert Advice on Maximizing the Calculator's Potential
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to New York Times Calculator Rent vs Buy
The New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator is a powerful tool designed to assist individuals in evaluating the financial aspects of renting versus buying a home. This calculator considers a wide range of variables, including property prices, mortgage rates, rental costs, and other related expenses, to provide users with a clear picture of which option suits their financial goals best.
Understanding the nuances of the housing market can be overwhelming, especially for those who are unfamiliar with financial terminology. This calculator simplifies the process by breaking down complex financial data into digestible information that anyone can understand. By using this tool, you can make a more informed decision about your housing needs and ensure that you're making the best financial choice for your future.
How the New York Times Calculator Works
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Calculator
Using the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator is straightforward and user-friendly. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
- Input your current financial information, such as your income, savings, and existing debts.
- Enter the estimated cost of the property you're considering purchasing, along with the expected mortgage rate and down payment amount.
- Provide details about your current or potential rental situation, including monthly rent and any additional costs associated with renting.
- Specify the length of time you plan to stay in the property, as this can significantly impact the overall cost comparison.
- Review the results and analyze the financial implications of each option.
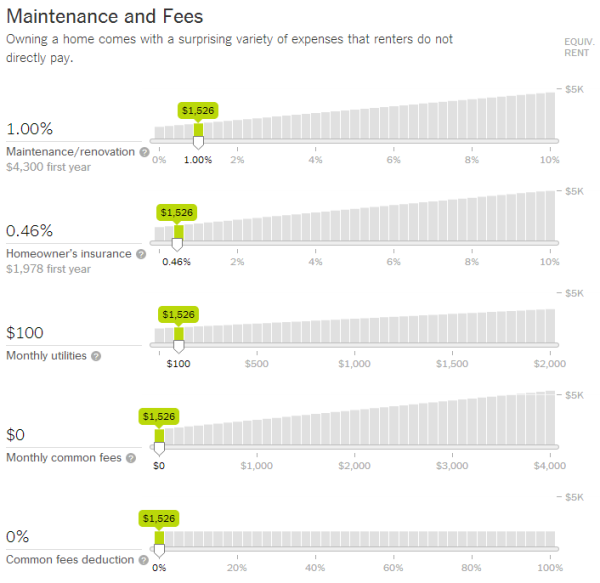
Key Factors Considered by the Calculator
The New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator takes into account several critical factors when determining the best housing option for you. Some of these factors include:
- Property prices and appreciation rates
- Mortgage interest rates and terms
- Rental costs and trends in your local market
- Taxes, insurance, and maintenance expenses
- Opportunity costs of investing in real estate versus other financial opportunities
By considering these factors, the calculator provides a comprehensive analysis of the financial implications of renting versus buying, helping you make a more informed decision.
Long-Term Benefits of Using the Calculator
Financial Planning and Stability
Using the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator can offer significant long-term benefits for your financial planning and stability. By understanding the financial implications of each option, you can:
Read also:Jenny Mollen Net Worth Discover The Wealth Behind The Multitalented Star
- Avoid making costly mistakes that could negatively impact your financial future
- Identify the best time to buy or rent based on market conditions
- Develop a more robust financial strategy that aligns with your long-term goals
Cost Comparison: Renting vs Buying
When comparing the costs of renting versus buying, it's essential to consider both short-term and long-term expenses. While renting may seem more affordable upfront, buying a home can offer significant financial benefits over time, such as equity building and potential tax deductions.
According to a report by The Federal Reserve, homeownership can lead to increased wealth accumulation over time compared to renting. However, it's crucial to weigh these benefits against the initial costs of purchasing a home, such as down payments, closing costs, and maintenance expenses.
Features of the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator
Advanced Financial Modeling
The New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator offers several advanced features that set it apart from other similar tools. These features include:
- Customizable inputs for personalized results
- Real-time updates based on current market conditions
- Graphical representations of cost comparisons for easy visualization
- Comprehensive breakdown of all associated costs, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using the Calculator
While the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator is an excellent tool, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that could lead to inaccurate results. Some of these mistakes include:
- Underestimating or overestimating your financial situation
- Ignoring local market conditions and trends
- Failing to account for unexpected expenses, such as repairs or property taxes
- Not considering the long-term implications of each option
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Successful Usage
Case Study 1: A First-Time Homebuyer's Journey
John, a first-time homebuyer, used the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator to evaluate his housing options. After inputting his financial information and considering local market conditions, he discovered that buying a home would be more financially beneficial in the long run. John was able to secure a mortgage and purchase a home that met his needs and aligned with his financial goals.
Case Study 2: A Seasoned Renter's Decision
Sarah, a seasoned renter, utilized the calculator to determine whether it was time to buy a home. After analyzing the results, she realized that renting was still the better option for her due to her frequent job relocations and lack of long-term commitment to a specific area. This insight allowed Sarah to continue renting without feeling pressured to purchase a home prematurely.
Expert Advice on Maximizing the Calculator's Potential
To maximize the potential of the New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator, consider the following expert advice:
- Regularly update your financial information to ensure accurate results
- Consult with a financial advisor to gain additional insights and guidance
- Stay informed about local market conditions and trends
- Use the calculator as a starting point for further research and decision-making
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The New York Times Rent vs Buy Calculator is an invaluable tool for anyone considering their housing options. By understanding the financial implications of renting versus buying, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your long-term goals and financial stability.
We encourage you to try the calculator and explore its features to determine the best housing option for your unique situation. Don't forget to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below, and feel free to explore other articles on our site for more valuable insights and information.