Understanding Michigan state tax rate is crucial for both residents and businesses operating in the state. Taxes play a significant role in shaping financial decisions, and having a clear grasp of the tax structure can help individuals plan their finances effectively. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of Michigan's tax system, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and more.
Whether you're a new resident, a business owner, or simply looking to enhance your knowledge of Michigan's tax policies, this guide will provide you with detailed insights. Our focus is to ensure you understand how these taxes affect your financial situation and how to navigate them efficiently.
This article aims to be a reliable source of information, adhering to the principles of E-E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life). We'll cover everything from the basics to advanced concepts, ensuring you have a complete understanding of Michigan's tax landscape.
Read also:Jenny Mollen Net Worth Discover The Wealth Behind The Multitalented Star
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Michigan State Tax Rate
- Michigan Income Tax Overview
- Sales Tax in Michigan
- Understanding Property Tax
- Business Taxes in Michigan
- Tax Exemptions and Credits
- Filing Your Michigan State Taxes
- Common Questions About Michigan Taxes
- Strategies for Effective Tax Planning
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Michigan State Tax Rate
Why Understanding Michigan Taxes Matters
Taxes are an essential part of living and doing business in Michigan. The state tax rate affects various aspects of life, including purchasing power, cost of living, and investment decisions. By understanding the Michigan state tax rate, individuals and businesses can better prepare for financial obligations and take advantage of available deductions and credits.
Michigan has a relatively straightforward tax system compared to other states, but it still requires careful attention to detail. This section will provide an overview of the main types of taxes in Michigan, setting the stage for more detailed discussions in subsequent sections.
Michigan Income Tax Overview
How Michigan Income Tax Works
The Michigan income tax rate is a flat 4.25% for all taxpayers as of 2023. This means that regardless of your income level, you will pay the same percentage of your earnings in state income tax. Unlike some states with progressive tax systems, Michigan's flat rate simplifies the calculation process for taxpayers.
Key Points:
- Flat rate of 4.25% for all taxpayers
- No deductions for federal income tax payments
- Supports deductions for retirement income under certain conditions
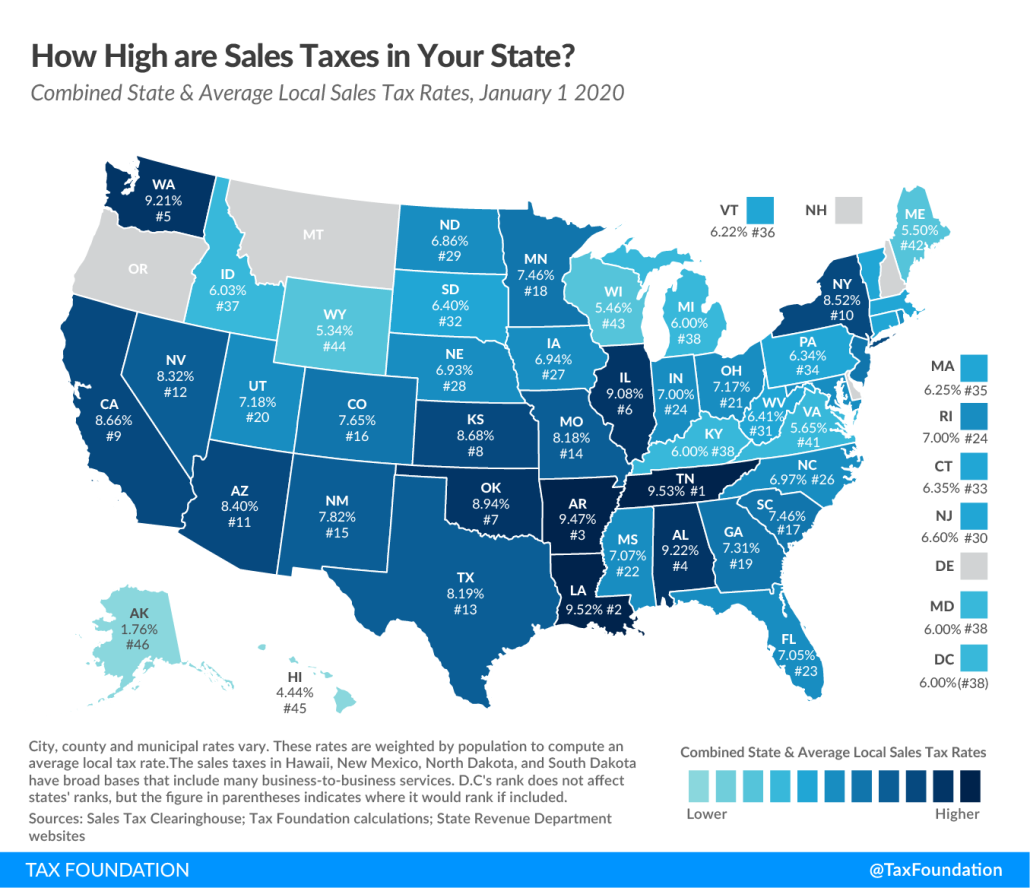
Sales Tax in Michigan
Understanding Michigan Sales Tax
Michigan imposes a statewide sales tax rate of 6%. This tax applies to most goods and services purchased within the state. However, there are exceptions, such as certain food items and prescription medications, which are exempt from sales tax. Understanding these exemptions can help consumers save money on essential purchases.
Common Exemptions:
Read also:Noodles Magazine A Comprehensive Guide To The Worlds Premier Noodle Enthusiast Publication
- Unprepared food items
- Prescription drugs
- Some medical devices
Understanding Property Tax
Property Tax Rates in Michigan
Property taxes in Michigan are calculated based on the assessed value of your property and the local millage rates. The assessed value is typically half of the market value, and millage rates vary by location. It's important to note that property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, funding schools, public services, and infrastructure.
Factors Affecting Property Tax:
- Assessed value of the property
- Local millage rates
- Homestead exemptions for primary residences
Business Taxes in Michigan
Taxes for Businesses in Michigan
Businesses operating in Michigan are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax, sales tax, and unemployment taxes. The Michigan Business Tax (MBT) was replaced by the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) in 2012, which applies to C corporations at a rate of 6%. Small businesses and partnerships may be taxed differently, depending on their structure.
Key Business Taxes:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
- Unemployment Insurance Tax
- Sales Tax for Goods and Services
Tax Exemptions and Credits
Available Exemptions and Credits in Michigan
Michigan offers several tax exemptions and credits to help reduce the tax burden for individuals and businesses. These include homestead property tax credits, senior citizen exemptions, and credits for low-income families. Understanding these benefits can help taxpayers save money and improve their financial situation.
Popular Credits:
- Homestead Property Tax Credit
- Senior Citizen Exemptions
- Working Income Tax Credit
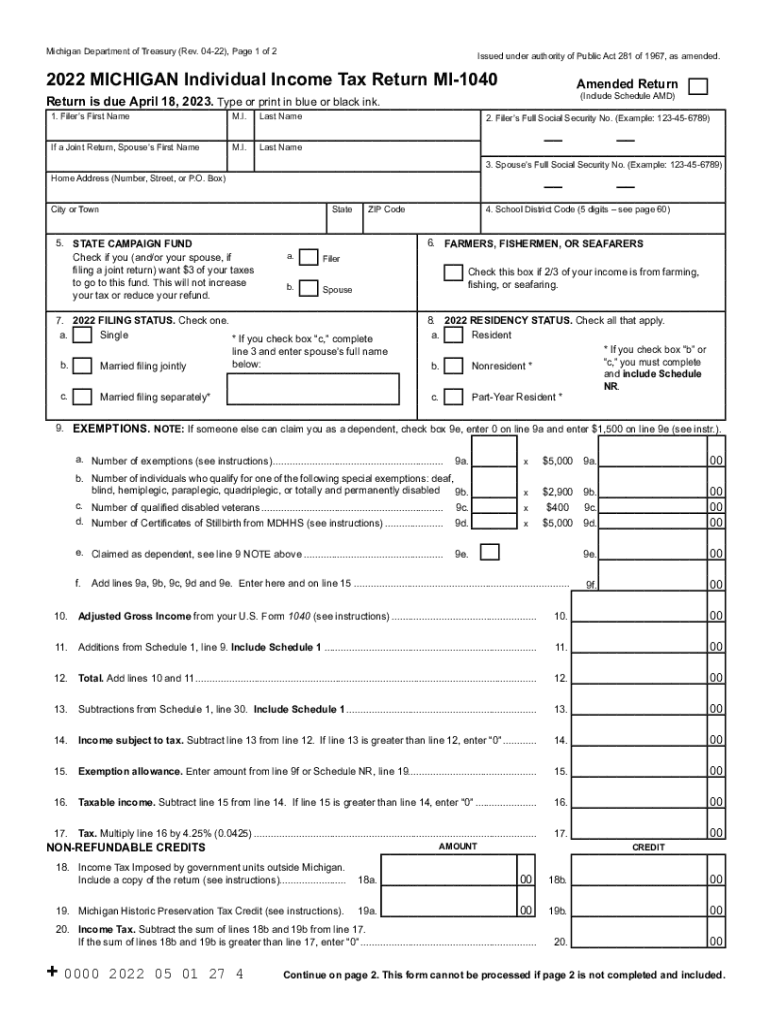
Filing Your Michigan State Taxes
Steps for Filing Michigan Taxes
Filing Michigan state taxes can be done through the Michigan Department of Treasury's website or using certified tax preparation software. It's important to gather all necessary documents, including W-2 forms, 1099s, and receipts for deductions, before starting the filing process. Filing electronically can expedite the refund process and reduce errors.
Tips for Filing:
- Gather all necessary documents
- Consider electronic filing for efficiency
- Double-check calculations and entries
Common Questions About Michigan Taxes
Frequently Asked Questions
Many taxpayers have questions about Michigan's tax system. Below are some common queries and their answers:
Q: Is Michigan a high-tax state? A: Michigan's tax rates are generally considered moderate compared to other states. The flat income tax rate and relatively low sales tax contribute to this perception.
Q: Can I deduct state taxes on my federal return? A: Yes, taxpayers can deduct Michigan state income taxes on their federal tax returns, subject to certain limitations.
Strategies for Effective Tax Planning
Maximizing Your Tax Savings
Effective tax planning is essential for minimizing your tax liability and maximizing your savings. Strategies include taking advantage of available deductions and credits, timing income and expenses strategically, and investing in tax-advantaged accounts. Consulting with a tax professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your financial situation.
Planning Tips:
- Utilize available deductions and credits
- Invest in tax-advantaged accounts
- Consult with a tax professional for personalized advice
Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding the Michigan state tax rate is vital for managing your finances effectively. Whether you're dealing with income tax, sales tax, property tax, or business taxes, this guide has provided comprehensive insights into each aspect. By staying informed and planning strategically, you can minimize your tax burden and make the most of your financial resources.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax situation, consulting with a tax professional if needed, and sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information. For more in-depth knowledge, explore additional resources and articles on our website.
Remember, staying updated on tax laws and regulations is crucial, as they can change annually. Keep yourself informed and empowered to make the best financial decisions for you and your family.