Have you ever wondered what second cousins are and how they fit into your family tree? Many people are familiar with the term "cousin," but the concept of second cousins often remains a mystery. As families grow and expand, understanding these relationships becomes increasingly important. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the meaning of second cousins, their place in genealogy, and how they connect to you through shared ancestors.
Learning about second cousins is not only fascinating but also essential for anyone interested in tracing their family history. Whether you're building a family tree or simply curious about your relatives, this article will provide all the information you need. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how second cousins fit into your family structure.
We'll delve into the intricacies of genealogical connections, explore the differences between first and second cousins, and explain how these relationships are determined. So, let's get started and uncover the mystery of second cousins!
Read also:What Did Suzanne Pleshette Die Of A Comprehensive Look At Her Life Career And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What Are Second Cousins?
- The Role of Genealogy in Understanding Second Cousins
- Biological Connection Between Second Cousins
- Building a Family Tree to Identify Second Cousins
- First Cousins vs. Second Cousins
- Degrees of Relationship in Family Trees
- Cultural Differences in Cousin Relationships
- Genetic Link Between Second Cousins
- Common Questions About Second Cousins
- Conclusion: Embrace Your Family Connections
What Are Second Cousins?
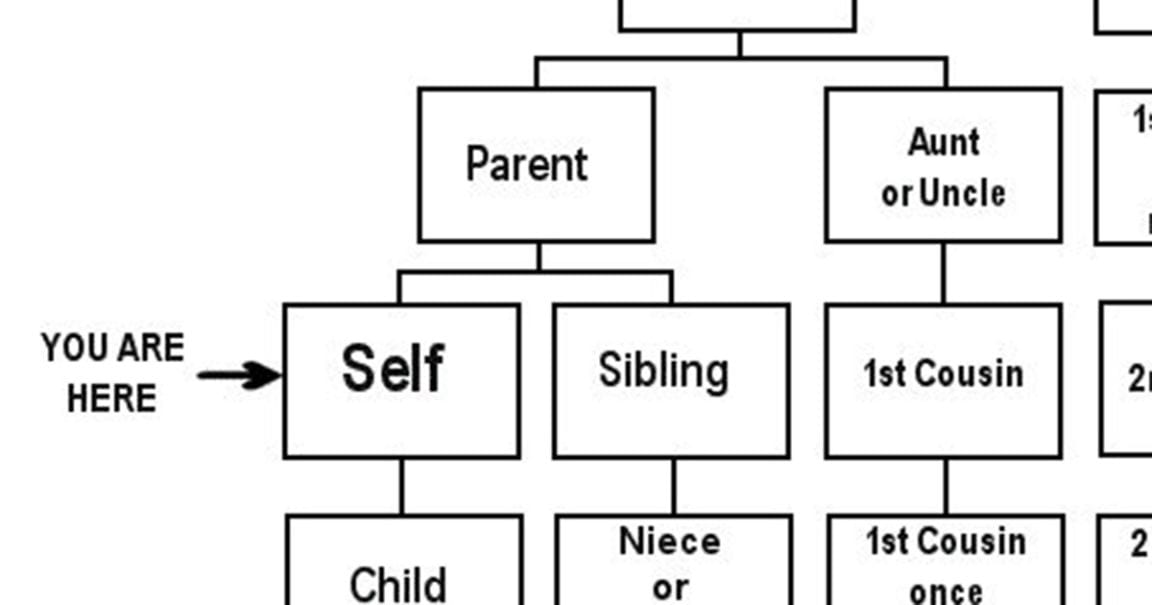
Second cousins are individuals who share the same great-great-grandparents but have no overlapping grandparents or parents. In simpler terms, your second cousin is the child of your parent's first cousin. This relationship is established through shared ancestors and is a crucial part of understanding your extended family tree. By tracing your lineage back to your great-great-grandparents, you can identify who your second cousins are.
How Second Cousins Are Related
The connection between second cousins is rooted in generational links. To clarify:
- Great-great-grandparents are the common ancestors of second cousins.
- Each second cousin's parent is a first cousin to the other.
- This means second cousins are two generations removed from the shared great-great-grandparents.
Understanding these connections helps clarify the complexities of family relationships and strengthens your genealogical knowledge.
The Role of Genealogy in Understanding Second Cousins
Genealogy plays a vital role in identifying and understanding second cousins. Through genealogical research, you can trace your family history and uncover the intricate web of relationships within your extended family. This process involves gathering information about your ancestors, documenting their lives, and mapping out how each family member is connected.
Tools for Genealogical Research
Modern technology has made genealogical research more accessible than ever. Here are some tools that can aid in your quest to understand second cousins:
- Ancestry.com: A popular platform for building family trees and connecting with distant relatives.
- 23andMe: A DNA testing service that provides insights into your genetic connections and potential second cousins.
- FamilySearch: A free genealogical database that offers extensive records and resources for tracing your ancestry.
By utilizing these resources, you can gain a deeper understanding of your second cousins and their place in your family tree.
Read also:Daria Sergeyevna Gordeevagrinkova A Detailed Exploration Of Her Life And Achievements
Biological Connection Between Second Cousins
The biological connection between second cousins is rooted in shared DNA. Since second cousins share the same great-great-grandparents, they inherit a portion of their DNA from these common ancestors. While the genetic link is weaker than that of immediate family members, it still exists and can be traced through DNA testing.
Percentage of Shared DNA
On average, second cousins share approximately 3.125% of their DNA. This percentage can vary slightly depending on the specific genetic inheritance patterns within families. DNA testing services like 23andMe and AncestryDNA can provide detailed insights into the amount of shared DNA between second cousins, helping to confirm these relationships.
Understanding the biological connection between second cousins not only strengthens family bonds but also offers valuable insights into your genetic heritage.
Building a Family Tree to Identify Second Cousins
Creating a family tree is an excellent way to identify and understand second cousins. By mapping out your lineage, you can visually see how each family member is connected and pinpoint the exact relationships between individuals. This process involves gathering information about your ancestors, documenting their lives, and organizing the data into a clear and concise format.
Steps to Build a Family Tree
Here are some steps to help you build a comprehensive family tree:
- Start with yourself and work backward, gathering information about your parents, grandparents, and great-grandparents.
- Document key details such as birth dates, marriage dates, and death dates for each family member.
- Use genealogical software or online platforms to organize your data and create a visual representation of your family tree.
- Reach out to relatives for additional information and collaborate with them to fill in any gaps in your research.
By building a family tree, you can easily identify your second cousins and gain a better understanding of your extended family connections.
First Cousins vs. Second Cousins
While both first and second cousins share common ancestors, there are distinct differences in their relationships. First cousins are the children of your parents' siblings, while second cousins are the children of your parent's first cousins. This means that first cousins are one generation closer to the shared grandparents, whereas second cousins are two generations removed.
Key Differences Between First and Second Cousins
Here are some key differences between first and second cousins:
- First cousins share the same grandparents, while second cousins share the same great-great-grandparents.
- The genetic connection between first cousins is stronger, with an average shared DNA of 12.5%, compared to 3.125% for second cousins.
- First cousins are more likely to have direct interactions and shared experiences, whereas second cousins may have limited contact due to generational differences.
Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the nuances of cousin relationships and strengthens your genealogical knowledge.
Degrees of Relationship in Family Trees
In genealogy, degrees of relationship refer to the number of steps between two individuals in a family tree. For example, first cousins are one degree apart, while second cousins are two degrees apart. This system helps organize and categorize family relationships, making it easier to understand complex connections within extended families.
Calculating Degrees of Relationship
To calculate the degree of relationship between two individuals, follow these steps:
- Determine the closest common ancestor shared by both individuals.
- Count the number of generations between each individual and the common ancestor.
- Add the two numbers together to determine the degree of relationship.
For instance, second cousins are two generations removed from their shared great-great-grandparents, making them two degrees apart. This method can be applied to any family relationship, providing a clear and consistent way to categorize connections.
Cultural Differences in Cousin Relationships
Cultural differences can significantly impact how cousin relationships are perceived and treated. In some cultures, cousin relationships are highly valued and play a central role in family dynamics, while in others, they may be less emphasized. These variations highlight the importance of understanding cultural contexts when exploring family connections.
Examples of Cultural Approaches to Cousin Relationships
Here are some examples of how different cultures approach cousin relationships:
- Indian Culture: In many Indian communities, cousin marriages are common and considered a way to strengthen family bonds.
- Western Cultures: In Western societies, cousin relationships are often viewed as distant and less significant than immediate family connections.
- African Cultures: In some African traditions, cousins are treated as siblings and play a crucial role in family support systems.
By recognizing these cultural differences, you can gain a broader perspective on the significance of second cousins and other family relationships.
Genetic Link Between Second Cousins
The genetic link between second cousins is an essential aspect of understanding their relationship. As mentioned earlier, second cousins share approximately 3.125% of their DNA, which is inherited from their shared great-great-grandparents. This genetic connection can be traced through DNA testing and provides valuable insights into family history and ancestry.
Implications of Genetic Connections
The genetic link between second cousins has several implications:
- It confirms familial relationships and helps identify distant relatives.
- It offers insights into inherited traits and potential health risks.
- It strengthens family bonds by providing tangible evidence of shared ancestry.
By exploring the genetic link between second cousins, you can deepen your understanding of your family's history and heritage.
Common Questions About Second Cousins
Many people have questions about second cousins and their place in the family tree. Below are some frequently asked questions and their answers:
FAQs About Second Cousins
- How are second cousins related? Second cousins share the same great-great-grandparents but have no overlapping grandparents or parents.
- Can second cousins marry? In most countries, second cousins are allowed to marry, as their genetic connection is relatively distant.
- How much DNA do second cousins share? On average, second cousins share approximately 3.125% of their DNA.
These answers provide clarity on common concerns and misconceptions about second cousins, helping to deepen your understanding of these relationships.
Conclusion: Embrace Your Family Connections
In conclusion, understanding what second cousins are and their place in your family tree is an essential part of genealogical research. By exploring the biological, cultural, and genetic aspects of these relationships, you can gain a deeper appreciation for your extended family connections. Whether you're building a family tree or simply curious about your relatives, this knowledge will enrich your understanding of your ancestry.
We invite you to take action by sharing this article with your friends and family or leaving a comment below. Your feedback helps us improve and create more informative content. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site to further your genealogical journey. Together, let's embrace the beauty of family connections and the rich tapestry of our shared heritage.