The average height in the US is a topic of interest for many people, whether they're studying human biology, public health, or simply curious about societal trends. Height has long been associated with various factors, including genetics, nutrition, and overall well-being. As we delve deeper into this subject, we will explore what defines the average height in the United States and how it has evolved over time.
Height is not just a physical attribute; it reflects the broader health and living conditions of a population. Understanding the average height in the US involves examining data from reliable sources, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). These studies provide critical insights into how height varies across demographics, including age, gender, and ethnicity.
In this article, we will break down the average height in the US, explore the factors influencing it, and discuss its implications for public health. Whether you're a researcher, student, or simply curious, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to understand this important topic.
Read also:Rob Lowe Height Unveiling The True Measure Of A Hollywood Icon
Table of Contents
- Overview of Average Height in the US
- Key Statistics and Trends
- The Role of Genetics in Height
- Impact of Nutrition on Height
- Height Differences by Gender
- Height Variation Among Ethnic Groups
- Height Changes with Age
- Comparison with Global Averages
- Height and Public Health
- Future Trends and Predictions
- Conclusion
Overview of Average Height in the US
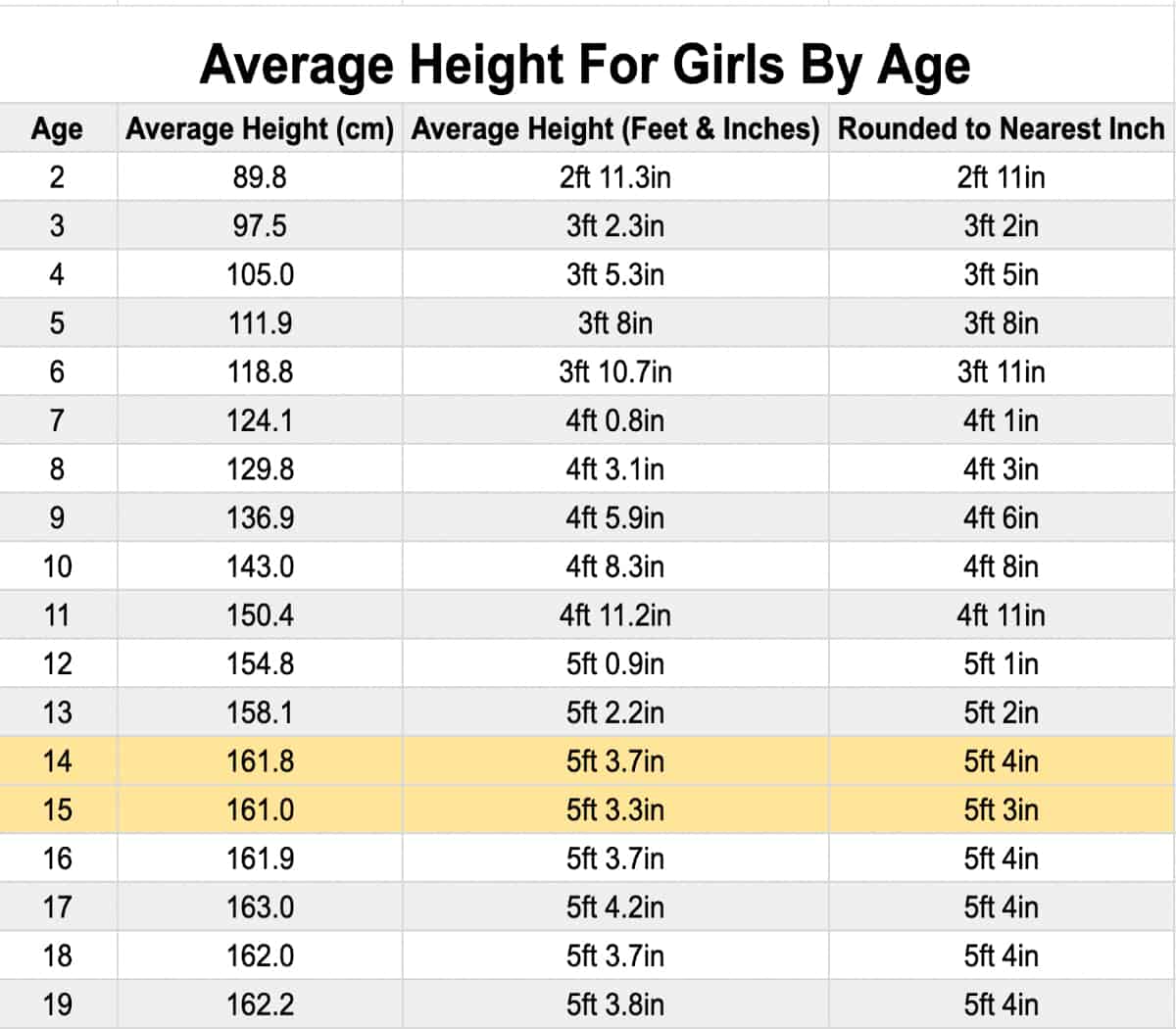
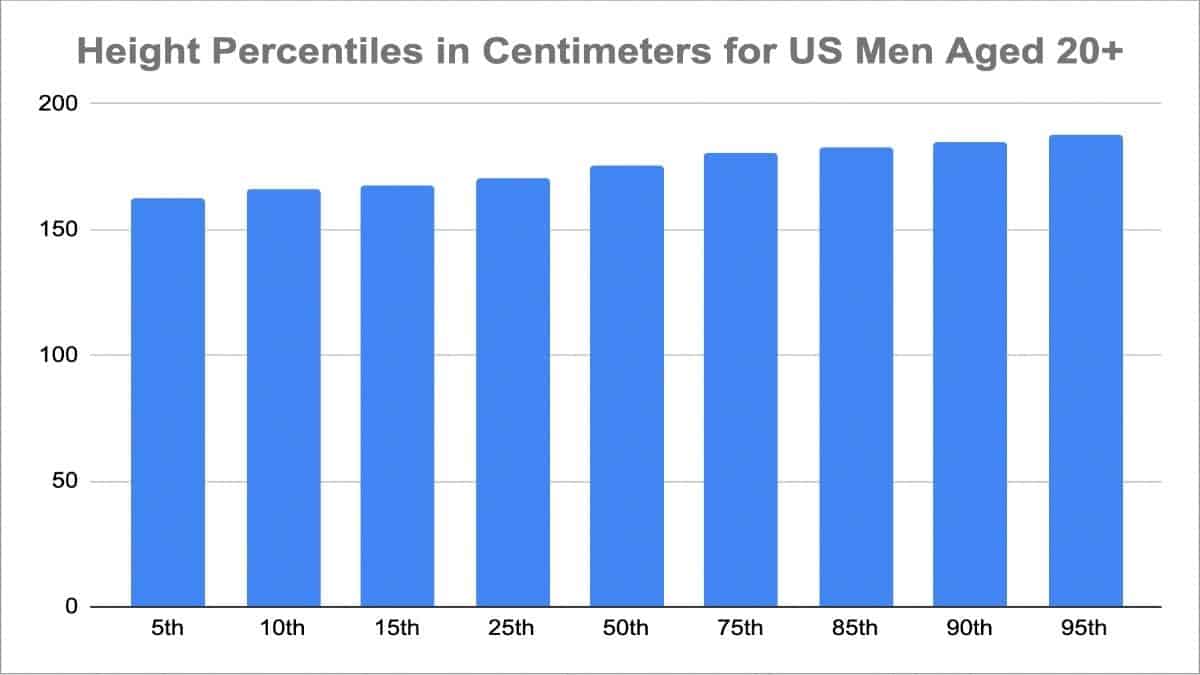
The average height in the US is a widely studied metric that reflects the overall health and development of the population. According to the CDC, the average height for adult men in the US is approximately 5 feet 9 inches (175.3 cm), while for women, it is about 5 feet 4 inches (162.5 cm). These figures are based on data collected from NHANES, a program that conducts surveys to assess the health and nutritional status of Americans.
How Height is Measured
Height is typically measured using standardized methods to ensure accuracy and consistency. Factors such as posture and footwear can influence measurements, so researchers follow strict guidelines to eliminate discrepancies. The average height in the US is calculated by analyzing data from large, representative samples of the population.
Significance of Average Height
Understanding the average height in the US provides valuable insights into the health and living conditions of its citizens. Height is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, making it a key indicator of overall well-being. Additionally, height trends can help identify disparities in health outcomes across different demographic groups.
Key Statistics and Trends
Data on the average height in the US reveals interesting patterns and trends over time. For instance, the average height of Americans has increased significantly since the early 20th century, largely due to improvements in nutrition and healthcare. However, this trend has leveled off in recent decades, prompting researchers to investigate potential reasons for stagnation.
Historical Perspective
- In the early 1900s, the average height for men was around 5 feet 7 inches, while for women, it was approximately 5 feet 2 inches.
- By the mid-20th century, average heights had increased to 5 feet 8 inches for men and 5 feet 3 inches for women.
- Today, the average height remains relatively stable, with minor variations across different population groups.
Current Trends
Recent studies suggest that the average height in the US has plateaued, possibly due to factors such as socioeconomic disparities and lifestyle changes. While improvements in healthcare and nutrition continue to benefit many, certain groups may still face barriers to achieving optimal height potential.
The Role of Genetics in Height
Genetics plays a significant role in determining an individual's height. Research indicates that approximately 60-80% of height variation is attributable to genetic factors. However, the remaining 20-40% is influenced by environmental factors such as nutrition, healthcare access, and living conditions.
Read also:How To Replace Bathtub Faucet A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners
Hereditary Factors
Height is influenced by multiple genes, with each contributing a small effect. Variations in these genes can result in differences in height among individuals. Family history is a strong predictor of height, as children tend to resemble their parents in stature.
Genetic Studies
Advances in genetic research have identified specific genes associated with height, such as those involved in bone growth and development. These discoveries have deepened our understanding of the complex interplay between genetics and environment in shaping human height.
Impact of Nutrition on Height
Nutrition is a critical factor in determining height, particularly during childhood and adolescence when growth is most rapid. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports healthy bone development and ensures that individuals reach their full height potential.
Key Nutrients for Growth
- Calcium: Essential for bone strength and development.
- Vitamin D: Facilitates calcium absorption and promotes bone health.
- Protein: Provides the building blocks for tissue growth and repair.
- Iron: Supports overall health and energy production.
Nutritional Challenges
Despite improvements in nutrition, some populations in the US still face challenges such as food insecurity and limited access to healthy foods. These issues can hinder growth and contribute to disparities in average height across different socioeconomic groups.
Height Differences by Gender
Men and women in the US exhibit notable differences in average height, with men generally being taller than women. This disparity is largely due to biological differences, including hormonal influences and genetic factors.
Biological Factors
Testosterone, a hormone present in higher levels in men, plays a role in promoting bone growth and overall height. In contrast, estrogen, which is more prevalent in women, tends to limit growth by closing growth plates earlier in life.
Social Implications
Height differences between genders can have social and cultural implications, influencing perceptions of attractiveness, leadership, and other traits. Understanding these dynamics is important for promoting equality and reducing gender-based stereotypes.
Height Variation Among Ethnic Groups
Height varies significantly among different ethnic groups in the US, reflecting differences in genetics, culture, and socioeconomic status. For example, individuals of Asian descent tend to be shorter on average compared to those of European descent.
Ethnicity and Genetics
Genetic variations among ethnic groups contribute to differences in average height. However, environmental factors such as nutrition and healthcare access also play a crucial role in shaping height outcomes.
Socioeconomic Influences
Disparities in socioeconomic status can lead to variations in height among ethnic groups. Access to quality healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living conditions are critical for achieving optimal height potential.
Height Changes with Age
Height is not static throughout a person's life; it changes significantly during childhood and adolescence before stabilizing in adulthood. However, factors such as aging and lifestyle can cause height to decrease later in life.
Childhood Growth Patterns
Children experience rapid growth during their early years, with growth spurts occurring during puberty. Proper nutrition and healthcare are essential during this period to ensure healthy development.
Aging and Height Loss
As people age, they may experience a gradual loss of height due to factors such as bone density loss and spinal compression. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help mitigate these effects.
Comparison with Global Averages
The average height in the US is comparable to that of other developed countries but lags behind some nations with particularly tall populations, such as the Netherlands. Global comparisons highlight the importance of addressing health and socioeconomic disparities to improve height outcomes worldwide.
International Trends
Studies show that countries with strong healthcare systems and high standards of living tend to have taller populations. These findings underscore the need for policies that promote equitable access to healthcare and nutrition.
Lessons from Other Countries
Nations like the Netherlands have achieved remarkable success in increasing average height through investments in public health and education. Their experiences offer valuable lessons for improving height outcomes in the US and beyond.
Height and Public Health
Height is closely linked to public health, as it reflects the overall well-being of a population. Factors such as malnutrition, chronic illness, and socioeconomic inequality can negatively impact height and contribute to disparities in health outcomes.
Health Implications
Short stature can be an indicator of underlying health issues, such as poor nutrition or chronic disease. Conversely, taller individuals may face increased risks of certain conditions, such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. Understanding these relationships is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.
Policy Recommendations
To address height disparities and improve public health, policymakers should focus on initiatives that promote equitable access to healthcare, nutrition, and education. These efforts can help ensure that all individuals have the opportunity to reach their full height potential.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, researchers expect the average height in the US to remain relatively stable, with minor fluctuations influenced by demographic changes and advancements in healthcare. However, addressing persistent disparities in height outcomes will require continued attention and action.
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies, such as personalized medicine and advanced nutritional supplements, may offer new opportunities to optimize height potential. These innovations could help level the playing field for individuals facing barriers to growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
While progress has been made in understanding and addressing height disparities, significant challenges remain. By focusing on equity and innovation, the US can work towards a future where all individuals have the opportunity to thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the average height in the US is a complex and multifaceted topic influenced by a range of genetic, environmental, and social factors. By examining trends, statistics, and research findings, we gain valuable insights into the health and well-being of the population. As we move forward, it is essential to address disparities and promote equitable access to resources that support healthy growth and development.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles and stay informed about the latest developments in public health and human biology.